
what are the requirements for kidney transplant؟
Kidney transplant criteria typically include having a long-term kidney disease. This is called by experts an End Stage Renal Disease and refers to a stage in which complete kidney failure happens. Several kidney ailments can result in End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD). Here, we will discuss this life-changing surgery and what it requires for kidney recipients and donors. Kidney transplantation is a cornerstone in modern medicine, heralded as the foremost organ transplantation surgery. It's advent has revolutionized healthcare, bestowing countless individuals with renewed hope and extended lifespans. Through this remarkable procedure, innumerable lives have been salvaged, offering a testament to its profound impact on humanity. So, we need to delve into Kidney transplant criteria as a lifesaver for ESRD patients.
What is the criteria for kidney transplant listing?
For kidney transplant surgery, you must take many factors into account which could be divided into two categories: Legal and medical considerations.In most countries, there are strict regulations for accepting a donor for transplantation, for example, the donor must be a first-degree family member, or there must be no financial transactions between them, etc., but there are also countries that have simpler rules for kidney transplantation, for example, Iran has very convenient laws which are limited to requiring a same nationality for donor and recipient. In the article about kidney transplant in Iran for foreigners, you can find more insights regarding this subject. This combined with its short waiting list and affordable costs, makes this country a perfect destination for kidney transplant surgeries.
In the context of determining the medical necessity for a kidney transplant, both the kidney transplant recipient and the renal donor criteria play pivotal roles. Assessing medical necessity involves a rigorous examination of the patient's health status against the kidney transplant criteria to ensure that transplantation is the most appropriate treatment option. Concurrently, the renal donor criteria are meticulously applied to identify potential donors who meet the stringent health and compatibility standards required for a successful transplant. This dual-layered evaluation process underscores the importance of a comprehensive understanding of both sets of criteria to optimize patient outcomes and transplant success rates.
In short, kidney transplant medical requirements encompass various criteria ensuring the suitability of both donors and recipients for successful transplantation. Prospective living donors must meet age requirements, demonstrate commitment to the donation process, and undergo rigorous physical and psychological evaluations to ensure compatibility. Compatibility extends beyond the willingness to include optimal health conditions and matching blood types. Furthermore, tissue typing evaluates the degree of compatibility between donor and recipient, with HLA antigens playing a crucial role. Additionally, body mass index (BMI) is a significant factor in transplant outcomes, with both high and low BMIs associated with increased risks. HLA typing and crossmatching are essential steps in the transplant process, aimed at identifying compatible donors and reducing the risk of rejection. You can explore the early signs of kidney rejection here. We will further delve into these requirements in the following sections.
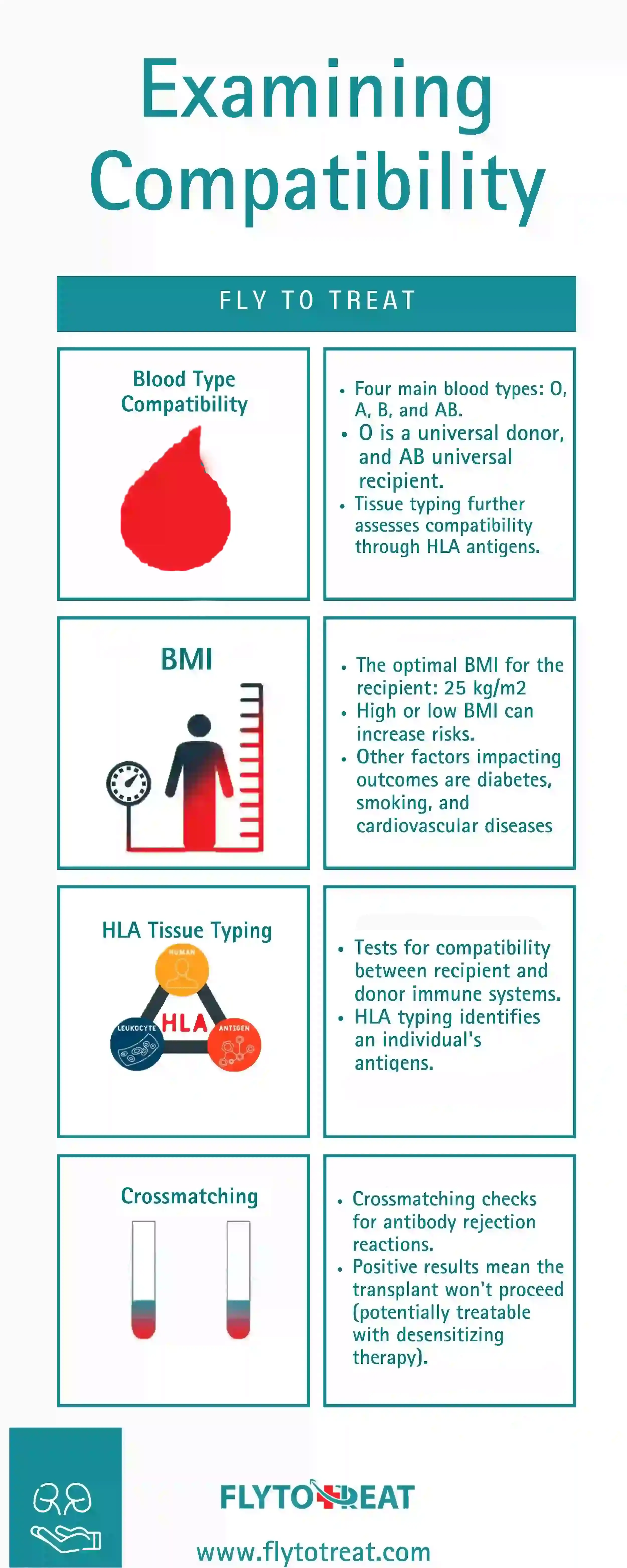
Kidney transplant requirements blood type
Before considering a kidney transplant operation, medical professionals conduct thorough evaluations to assess the severity and progression of the kidney disease. Besides, the kidney transplant operation must have a good chance of success. Also, the patient must be able to take the required daily medicines needed after a kidney transplant, including immunosuppressant medication.The human body possesses four primary blood types: O, A, B, and AB. Among these, type O holds the distinction of being the most prevalent, followed by type A, type B, and lastly, the rarest, type AB. For successful organ transplantation, the recipient's blood type must harmonize with that of the donor. The congruence criteria for blood type transplantation mirror those of blood transfusion. While some blood types are compatible with donation, others are not. Type O is regarded as the universal donor, meaning individuals with type O blood can donate to recipients with any blood type. Conversely, type AB is termed the universal recipient, signifying that individuals with type AB blood can receive organs or blood from donors with any blood type. The chart below provides a clear depiction of blood type compatibility for donation.
HLA tissue typing for kidney transplant
HLA typing and crossmatching are essential steps in the kidney transplant operation. HLA stands for Human Leukocyte Antigen, which are proteins found on the surface of cells. Human Leukocyte antigens are responsible for identifying the body's cells from foreign cells.
HLA typing involves identifying the Human Leukocyte antigens of both the kidney recipient and the potential donor. This is done by analyzing blood samples from both individuals. The goal of HLA typing is to find a donor whose HLA is as similar as possible to that of the recipient.
There are two types of crossmatching:
Complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC):
This is the traditional method of crossmatching. It uses complement, a protein found in the blood, to detect antibodies in the recipient's serum that bind to the donor's cells. A positive CDC crossmatch indicates that the recipient's immune system will likely reject the donor's kidney.
Flow cytometry crossmatches (FCXM):
This is a newer method of crossmatching that is more sensitive than CDC crossmatching. It uses flow cytometry, a technique that allows for the identification and analysis of individual cells, to detect antibodies in the recipient's serum that bind to the donor's cells. A positive FCXM also indicates that the recipient's immune system will likely reject the donor's kidney.
Kidney transplant BMI
It's crucial to understand how body mass index (BMI) aligns with kidney transplant criteria and renal donor criteria. A high BMI at the time of transplantation is associated with an elevated risk of post-renal transplant surgery mortality, graft failure, delayed graft function, and various surgical complications. Similarly, low BMI levels have been demonstrated to contribute to diminished post-renal transplant surgery outcomes, which in some instances may be linked to frailty and sarcopenia. There is a well-established "U-shaped" relationship between BMI and renal transplant surgery outcomes for kidney recipients, which is 8-11 Overall.
You can check the best diet for kidney transplant patients to keep your BMI fit.
What GFR Level Requires Transplant?
A GFR (glomerular filtration rate) below 15 indicates severe kidney failure, necessitating dialysis or a kidney transplant. This level marks stage 5 kidney disease, where kidney function is critically impaired. Understanding these transplant list requirements helps patients and healthcare providers prepare for necessary interventions. Knowing the exact requirements for kidney transplant and how they align with specific kidney transplant match criteria is crucial for timely and effective treatment.
What is the standard criteria donor for kidney transplant?
Specific criteria must be met to qualify for a healthy kidney from a living donor. Firstly, the individual must be over 18 years old, ensuring legal capacity and maturity in decision-making. Moreover, they must exhibit a steadfast commitment to the kidney donation process, encompassing the pre-donation evaluation, surgical procedure, and subsequent recovery phase.
In addition to willingness, the prospective donor must undergo thorough physical and psychological assessments to ascertain their suitability for organ donation. This involves ensuring optimal health conditions, both physically and mentally, to mitigate risks associated with the donation process and to safeguard the donor's well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding the qualifications for kidney transplant list inclusion is crucial for potential candidates. FlyToTreat provides comprehensive answers to questions like "Kidney transplant requirements blood type" and "What GFR level requires transplant?" Meeting the specific requirements for kidney transplant and navigating the kidney transplant match criteria can significantly impact the success of the procedure. FlyToTreat offers detailed information and guidance to help you through this critical journey, ensuring you have all the necessary knowledge to proceed with confidence.
MEDICALLY REVIEWED BY: Dr. Ali Bazazi
AUTHOR: FlytoTreat's team of Authors
07 February 2024 - Updated At: 03 August 2024
Related Articles
Comment





